What Is Scoliosis – And What Can Be Done?
What Is Scoliosis – And What Can Be Done?: Alex Szabo – Nottingham Osteopath
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that usually occurs during the growth spurt just before puberty. If you are interested in Scoliosis treatment, you’ve come to the right place. Using Schroth therapy together with a range of manual interventions and shockwave therapy treatment such as the Gymna ShockMaster, Scoliosis can be treated with promising results.
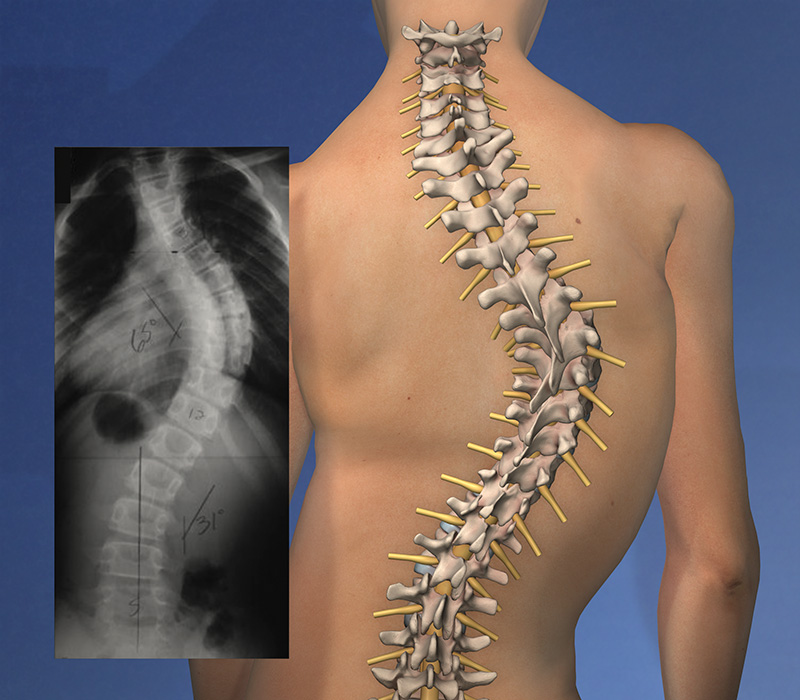
Scoliosis sufferers have a spine which spine curves to the right or left. Scoliosis produces a primary curve which is the one with the greatest angle and also compensation curves usually above and/or below the main curve. Most often, the scoliosis is shaped like an S a reversed S. However, it can also be a long C-shaped curve with a slight compensation in the neck and/or transition to the pelvis.
Spotting Scoliosis
Most people ask “what is scoliosis”, many have never even heard of the condition, despite it being quite common. There are some telltale signs to look for when deciding whether a person has scoliosis. The shoulder on the side where the upper curve is (the thoracic at the ribs) is usually higher than the other, and it is also slightly tilted forward. You will see that the shoulder blade is backward (winging).
The muscles on the convex side (where the curve is) will appear clamped, however, this is due to the rotation in the back of the spine which occurs concurrently with the development of the curve. This rotation can be viewed from the side where it looks like an increased curvature backwards.
The Pelvis and Hips
There may be a shift to the right or left. In some people, however, the pelvis is balanced so that this displacement does not occur.
Scoliosis may occur as a secondary disorder, to neuromuscular diseases for example. However, in 75-80% of cases, the origin is unknown.
Scoliosis can be divided into Structural and Functional scoliosis.
Structural
Structural scoliosis means that there are structural changes. In structural scoliosis, rotation of the spine will always occur in the area of the curve.
- Idiopathic (75% -80%)
- Neuromuscular (5% -7%)
- Congenital (10%)
- Recklinghausen (2% -3%)
- Others (Marfan, Beals,… tumours)
Functional
Functional scoliosis occurs as compensation for another condition in the body. For example, it can be a bone length difference that makes the back look skewed. In a forward bend, however, one can see that there is no rotation of the spine.
3-5% of children and adolescents have scoliosis. However, not everyone is requiring treatment. Scoliosis is defined as a lateral curve with Cobb’s angle of 10 degrees or more and rotation of the spine.
Girls are 10 times more vulnerable to getting scoliosis that develops as boys.
Scoliosis is not a dangerous disease, and most people live normal, active and good lives. When the diagnosis is made, the person should be referred to a physiotherapist specializing in the area.
The treatment of scoliosis depends on the person’s age, Cobb’s angle
Nottingham Osteopath Alex Szabo provides osteopathy and sports massage treatments for patients across the Midlands.
QUICK CONTACT
Tel: 0747 124 8330
Email: info@nottsosteopathy.co.uk
Office Hours: Mon-Fri 7am - 7pm


